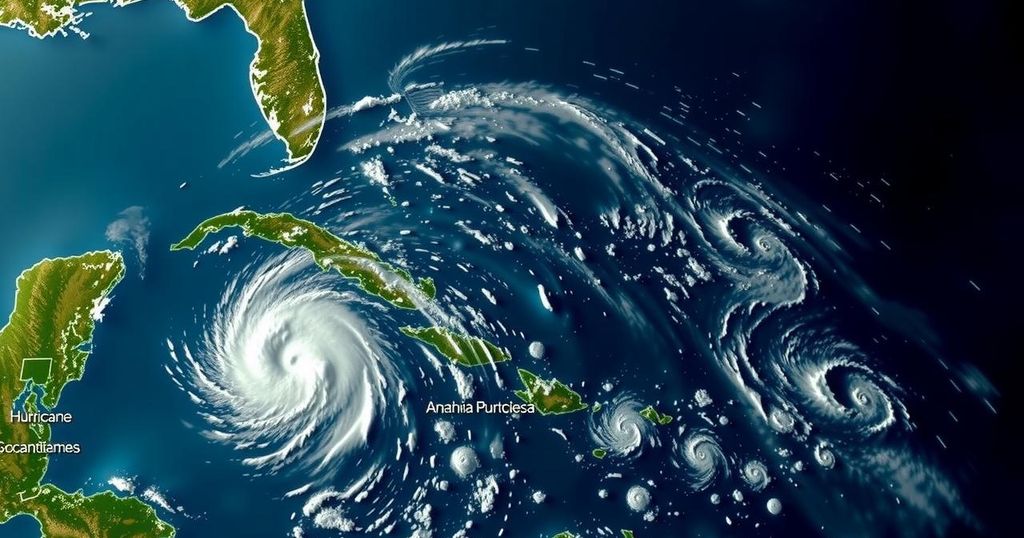
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season was unprecedentedly active, yielding 18 named storms, 11 hurricanes, and five major hurricanes. Key storms included Beryl, Helene, Milton, and Rafael, each of which set records and caused significant impacts across the United States. This season witnessed exceptional occurrences such as simultaneous hurricanes and late-season activity in the Gulf, emphasizing changing patterns in hurricane behavior.
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season has concluded with a record number of named storms and hurricanes. Forecasters correctly anticipated high activity due to warm sea-surface temperatures and the cessation of El Niño effects. A total of 18 named storms emerged, including 11 hurricanes and five major hurricanes. Major storms included Hurricane Francine, which made landfall in Louisiana, and Helene and Milton, both of which made landfall as major hurricanes elsewhere in the U.S.
Hurricane Beryl, the earliest Category 5 hurricane on record, made landfall in July, causing flooding and power outages as far away as Texas. Hurricane Helene struck Florida’s Big Bend region with devastating effects, leading officials to categorize it as the deadliest hurricane in the U.S. since Katrina in 2005. With over 150 fatalities, the storm also marked an unprecedented prediction by the National Hurricane Center.
Hurricane Milton astonished researchers by undergoing rapid intensification, leading to a maximum wind speed of 180 mph, before making landfall as a Category 3 storm. It is notable for enabling the first occurrence in recorded history of three concurrent hurricanes in the Atlantic during October.
Hurricane Rafael, while less intense, was significant as late-season hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico are exceedingly rare. Its appearance is part of a pattern wherein 12 named storms developed after the season’s peak, with seven hurricanes forming in the latter part of the season — a new record.
Overall, the 2024 season was remarkable not only for its number of storms but also for the substantial impacts they had on the U.S.
The Atlantic hurricane season is an annual event that typically spans from June 1 to November 30. Each year, meteorological organizations, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), monitor storm activity closely. In 2024, various climatic conditions contributed to an exceptionally active season. With record-breaking occurrences of named storms and hurricanes, this season exemplified significant changes in hurricane behavior, intensity, and landfall effects, highlighting the ongoing impacts of climate factors.
In conclusion, the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season was historic, as it produced an unprecedented number of named storms and hurricanes, with significant impacts across the United States. Major events such as Hurricanes Beryl, Helene, Milton, and Rafael illustrated the changing nature of hurricane activity, particularly with the occurrence of simultaneous hurricanes and the emergence of late-season storms in the Gulf. This season serves as a reminder of the potential for increased hurricane activity and related impacts in future cycles.
Original Source: www.nola.com